SAP® is embedding Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into its business applications, enabling developers & data scientists to use the Business Technology Platform (BTP) to create intelligent data models and forecasts to use in day-to-day operations. Read on to learn the differences between AI and ML and how to identify situations to benefit your business.
The Upside of COVID
“Was I deceived or did a sable cloud Turn forth her silver lining on the night?”
– John Milton, 1634
The modern version is shorter but loses the poetry: “Every cloud has a silver lining.”
While COVID-19 has had a devastating impact on life as we know it, it’s also fast-tracked adoption of digital transformation and technologies like cloud, artificial intelligence, robotics, blockchain, Internet of Things (IOT), and 3D printing.
Machine Learning Aims to Eliminate Routine Work
Machine Learning – another of those fast-tracked technologies – is helping enterprise SAP S/4HANA users respond to customers, competitors, regulators and partners all while transforming their businesses into intelligent enterprises.
According to Gartner (2020), 69% of the routine work managers are doing will be fully automated by 2024. Machine Learning is critical for businesses wanting to get going on that automation.
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
What do all the terms mean?
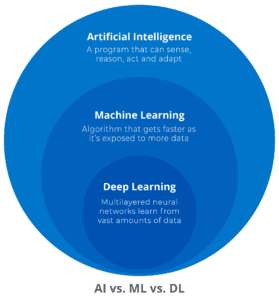
Artificial Intelligence
AI is a somewhat generic term for machines that mimic abilities usually found in humans – like solving problems or learning. Most AI is really a set of programmed instructions that tell a machine how to respond in specific situations.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a smaller subset of AI that detects patterns and learns how to make predictions and recommendations by processing data rather than relying on programming logic.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, where the learning is based on artificial neural networks that also require vast amounts of data.
SAP’s S/4 HANA in the AI/ML World
SAP is embedding AI into applications (S/4HANA and other apps) combining Robotic Process Automation (RPA), SAP Conversational AI, and SAP AI Business Services through its Business Technology Platform (BTP).
How is SAP’s AI different from Robotic Process Automation?
SAP’s ML predicts future outcomes in real-time using historical data, helping business users make accurate, timely decisions.
RPA automates repetitive, recurring non-value-added tasks, freeing up business users for more important work.
How Does ML work in SAP S/4HANA?
It uses customer-specific history and exceptions to predict future outcomes which can be used to automate decisions.
Which Business Problems Should it Solve?
Which business problems should and should not be solved by using ML? For problems being solved by ML, what’s the best approach?
If your business problem has no clear business logic to solve (or if the logic involves complex business rules) with historical data, it’s a good candidate for using ML. Predicting delivery times or segmenting sales prospects are good examples.
If there is clear business logic that can solve your business problem, you can instead use programming to solve it (like calculating inventory).
Implementing ML
Currently-available cloud platforms and 3rd-party data analytics tools enable just about any organization to implement a ML program.
SAP is embedding ML into its business applications and enabling developers and data scientists to create ML models through the Business Technology Platform (BTP).
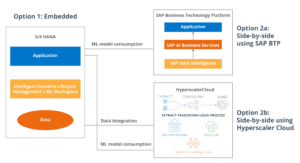
Two Kinds of ML in S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA has two ML capabilities: Embedded and Side by Side.
Embedded ML is great for simple processes that can use classic algorithms like clustering and classification using no external data. It’s based on SAP Analytics cloud.
Side-by-Side ML is for complex processes requiring deep learning, high CPU and RAM capacities, and incorporating external data. It’s based on the SAP Business Technology Platform.
Managing Machine Learning Scenarios
SAP’s Intelligent Scenario Management App (ISLM) offers an interface for managing ML models regardless of what data sources the model uses. It allows developers to train a ML model using existing customer data. Users can publish the model for use in other SAP Fiori applications.
ISLM comes with a number of sample ML scenarios including versions that automate sales orders, predict lead times, and predicts sales performance. The scenarios apply to different lines of business including finance, public services, sales, manufacturing, and more.
Other ideas for ML scenarios are available from SAP resources.
Let Computers be Computers
Using SAP S/4HANA Machine Learning models, users across all lines of business can let computers be computers. Use them to automate redundant tasks, process large data sets, make predictive decisions, or even automate entire processes.
And free up valuable employees to do the work that still requires a human touch.

