First things first.
People analytics.
Let’s define that phrase. It’s more than just people-watching at the local mall.
Research giant Gartner defines it as:
“The collection and application of talent data to improve critical talent and business outcomes. People analytics leaders enable HR leaders to develop data-driven insights to inform talent decisions, improve workforce processes and promote positive employee experience.”
While we can trace the origins of People Analytics back to the early 1900s, it came into its own in the 2000s with interest from companies like Google, Microsoft, and IBM.
Current State of People Analytics
Over the last decade, people analytics has grown from a “business extra” to a “can’t survive without” business need.
Today, 70% of companies invest in people analytics, but only 21% see the expected value.
And most companies are new to it. At Rizing, we’ve found that 70% of organizations started their people analytics program in the last 2-4 years.
But how do companies get a sense of where they are at with People Analytics?
Industry experts like Thomas Davenport have outlined how to conduct self-assessments. However, many analytical teams are too new to complete a self-assessment objectively.
Rizing’s People Analytics Maturity Model
At Rizing, we used existing research and industry expertise to develop our definitions of people analytics maturity. The definitions fall along a path. All organizations must start at the Foundational stage and get to the Leading stage as they develop their people analytics capabilities.
People Analytics Levels
1: Foundational | 2: Operational | 3: Insightful | 4: Strategic | 5: Leading |
| Organizations that haven't started or are about to start their analytics program | People analytics focused on providing point-in-time operational and compliance reports to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and timeliness. | People analytics are used to answer key business questions through identifying historical trends and determining where to take action. | People analytics are embedded in processes. Multiple data sources and types are combined to give insights into what is driving an outcome. HR program impacts can be evaluated. | Analytics are used to drive and predict outcomes, prescribe actions, evaluate the results of what-if scenarios, and make strategic decisions. |
| We can't easily report on how diverse our hiring is. | We know how diverse our hiring is. | We are learning what stages of hiring impact different diversity groups. | We understand the key drivers and where to invest in diverse hiring. | We can predict how different programs and actions will improve diverse hiring. |
There are two important considerations when interpreting analytics maturity levels:
Goals and Definitions
- Don’t try to be an analytics leader right away. Instead, work towards being Insightful or Strategic. Strive for a level three or four, then focus on maintaining it. You’ll still need to grow and improve to stay there.
- The definition of each level will evolve as new technologies and capabilities emerge. If an organization is stagnant, it’s possible to move down a maturity level because the definitions changed.
Get a baseline, then set a goal. Figure out your organization’s current level of maturity. Then determine what level to aim for to meet business needs and objectives.
Barriers and Challenges to Developing Analytical Capabilities
Rizing identified two common barriers and two common challenges that companies experience when developing analytical capabilities:
Barrier #1: Changes to the organization, leadership, or department
Losing a key sponsor, leader, or developer can stop a project. Especially if the project is young. These roles are critical for the success of new initiatives.
Connecting initiatives like developing analytical capabilities to the overall organizational strategy is crucial.
It’s equally important to retain key people. If they exit the project, either reassign the responsibilities or hire a replacement as soon as possible.
Barrier #2: Lack of investment in non-digital activities
Another common barrier is the lack of investment in non-digital activities:
- Immediate and ongoing training and support
- Documentation
- Ongoing updates
- Other change management activities
New analytical and digital initiatives often fall flat without the support of these non-digital activities.
Challenge #1: Not developing all areas together
Don’t just focus on the technology. Also, consider the social and organizational change involved when digital or analytical changes occur.
Challenge #2: Not realizing that maturity is a moving target
Don’t think analytical maturity is static with an endpoint. Instead, understand it’s a moving target. Experts in the industry are constantly advancing our understanding of analytical maturity.
Measuring Analytical Capabilities and Maturity
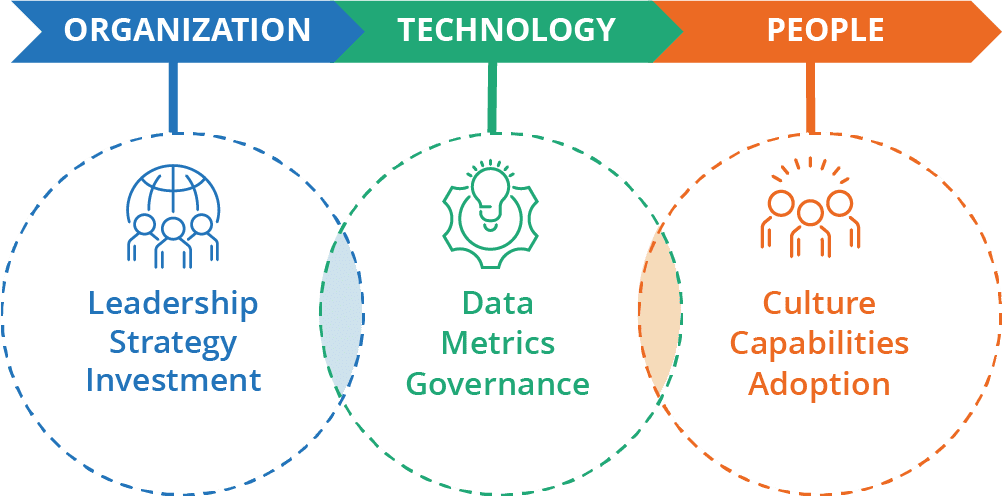
What do we measure regarding analytical capabilities and maturity? The intersection of organizations, technology, and people.
Rizing’s People Analytics Maturity Model (PAMM)
Advances in technology have significantly impacted how work gets done. New technology requires new processes, tasks, and expertise to deploy and maintain them.
This is part of the change that occurs when a new technology is brought into an organization.
Rizing’s people analytics maturity model starts with this change as the foundation. We then added change theory, systems thinking, and existing research to develop our model and assessment.
The result?
A reflective model able to predict the level of analytical maturity that an organization has achieved.
Key Drivers
Our model has three key drivers:
- Organizations
- Technology
- People
We evaluate these drivers with 23 variables that provide a deep understanding of your current analytical capabilities and highlight your strengths and weaknesses.
Rizing’s People Analytics Maturity Assessment (PAMA)
Rizing’s PAMA is a free, online 30-minute self-assessment. The results provide analytical and HR leaders with evidence outlining their capabilities and analytical maturity. The results also highlight their strengths and weaknesses and identify quick improvement wins.
Sample Results:
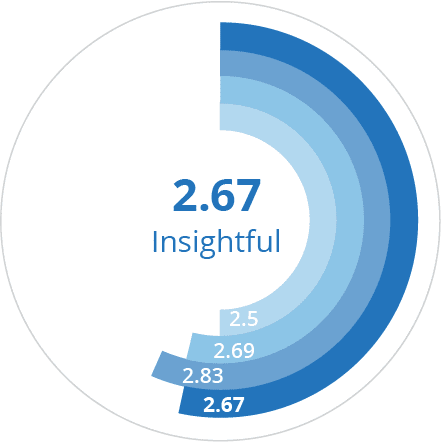 | 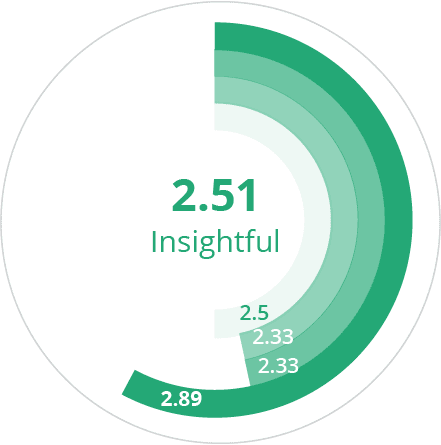 | 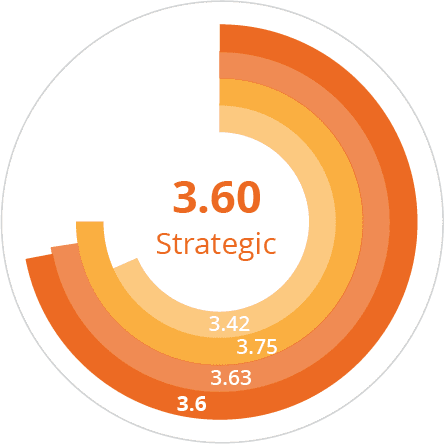 |
Organization 2.67 | Technology 2.89 | People 3.6 |
Strategy 2.83 | Metrics 2.33 | Culture 3.63 |
Leadership 2.69 | Data 2.33 | Capabilities 3.75 |
Investment 2.5 | Data Governance 2.5 | Adoption 3.42 |
Along with the final maturity score is a 10+ page report highlighting your current capabilities.
Common People Analytics Challenges
From our early assessments, we have identified the most common challenges that organizations face within each driver.
Organization | Technology | People |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy: There is an overall lack of decision-making within roles or a structure to support decision-making. | Data: Challenges around organizing domain-specific data and allowing for engineer access for different users. | Culture: There is a growing divide in corporate digital cultures and it's creating a digital skills gap. |
| Leadership: There is a level of awareness, but not enough practical understanding and use of analytics at senior leadership levels. | Metrics: Few organizations have standardized metrics, leaving data to be interpreted haphazardly. | Capabilities: Organizations are investing in hiring capabilities that may be beyond what's realistically achievable as defined by the organization. |
| Investment: Organizations don't invest in non-digital activities or linking the digital change to existing systems. | Governance: Organizations are overestimating their data governance capabilities and are open to unrealized risks. | Adoption: Perceptions can be affected by low levels of investment into change management or co-developing applications with end-users. |
Some more observations on the challenges that organizations face when improving their people analytics:
Organization
In the organization driver, we noticed these factors slowing down the adoption of analytics:
- Not understanding the types of decisions being made
- Needing different data for different roles
- The analytical team’s ability to present the right data to the right people at the right time
- Leadership’s willingness and ability to use analytics
- Not investing in non-digital activities to support analytics adoption
This is commonly the least mature driver, with an average score of 2.6.
People
One people-related challenge we noticed was the digital gap. It seems to be getting wider.
Nearly everyone works with technology, but not everyone works with personal computers. People that don’t use computers can lack critical digital and other skills needed to keep up with changes in HR technology.
Organizations also tend to burn through analytical talent. They aren’t realistic about necessary skills and over-hire. Talent doesn’t get to use their hard-earned skills. They end up disengaged and looking for new projects and opportunities.
People still tend to be one of the most mature business areas, with an average score of 3.4.
Technology
Most organizations, no matter how mature they are, struggle with:
- Data quality
- Integration
- Access
- Developing metrics
- Creating a standardized way to develop metrics
This driver has an average score of 2.8, but if we remove the governance scores, it falls to less than 2.4.
More About Rizing’s People Analytics Assessment
If you’re interested in learning more about where your organization falls in these different areas, consider taking our assessment. It’s easy to access online and you can complete the survey on your phone.
More about the survey:

- What: An online assessment using Qualtrics.
- How long: Takes ~30 minutes to complete.
- Turn around: Report returned in five business days.
- Why: Personalized insights and recommendations.
- Who: A head of/VP/Director of People Analytics should take the assessment.
- Report: Written for all senior-level HR Leaders.
- Follow-up: Clients will have a one-hour follow-up call with a Rizing expert to review the findings and help interpret the report.
Common Use Cases
- Measuring current capabilities as an assessment and benchmark.
- Complete assessment annually as part of an ongoing assessment/used as part of KPI.
- Before and after a major deployment or new initiative as part of measuring the impact of the project/measure of success.
Ready?
Ready to get started on your own People Analytics Maturity Assessment? Head over to the assessment request form to get started.